Sometimes all you need to get meaningful work done is a quiet corner and notepad. Others, you benefit from collaborative tools such as interactive whiteboards and video conferencing software.
Modern office technologies help support workers with exactly what they need to be productive in the moment, as well as keeping them safe and healthy. Use this guide to help you discover what’s possible.
What Is Office Technology?
Office technology refers to the hardware and software used in a workplace to enhance productivity, communication, and efficiency. It encompasses a wide range of devices and systems that work in concert to facilitate smooth day-to-day business operations.
Leveraging office management tools enables businesses to adopt the latest technology while maintaining a structured and organized workflow.
Main Types Of Office Technology
Nowadays, office technology often needs to support workforces that are a mix of in-office and remote, leading to a rise in tools like hot desk booking software.
Below I’ve grouped office technologies, both hardware and software, into the most common types:
Hardware
- Computers: Desktop PCs, laptops, and tablets.
- Printers, scanners, copiers: Devices for handling documents, printing, and scanning physical papers.
- Telecommunication equipment: Telephones, VoIP systems, video conferencing tools, etc.
- Network infrastructure: Servers, routers, and wireless systems for internet access and data sharing.
- Smart/IoT technologies: Smart office tech such as adaptive lighting, temperature control, and sensors to monitor traffic and space usage.
Software
- Office productivity tools: Word processing, spreadsheets, presentations (e.g., Microsoft Office, Google Workspace).
- Communication software: Email and instant messaging and collaboration tools (e.g., Slack, Miro).
- Office space management software: Systems like hot desk booking software, room reservation systems, and visitor management software.
- Project management software: Tools for organizing and tracking tasks (e.g., Trello, Asana).
- Enterprise systems: Customer relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and HR systems.
9 Must-Have Modern Office Technologies
While I consider a good coffee machine as the #1 must-have office tool, here are some other technologies that will help you create a productive, collaborative, efficient, safe, and smart office space.
1. Smart meeting rooms
Smart meeting rooms enable efficient scheduling, high-quality communication, and interactive brainstorming, enhancing collaboration for both in-person and remote teams.
Some examples include:
- Conference room equipment: Smart screen, large monitors, video conferencing systems, high-quality microphones, and speakers for virtual meetings.
- Interactive whiteboards: Smartboards or digital whiteboards for real-time collaboration during meetings and brainstorming sessions.
- Room scheduling systems: Digital room booking displays outside meeting rooms and integration with online calendars (e.g., Google Calendar) to reserve workspaces.
2. Unified communication systems
Disconnected communication tools can lead to missed messages and inefficiencies, but a unified system keeps teams connected no matter where they work.
By integrating calls, video, and collaboration into one system, businesses can streamline workflows and enhance productivity.
Examples include:
- VoIP phone systems: VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) phone systems replace traditional landlines and integrate voice calls, video conferencing, and messaging.
- Video conferencing tools: Systems like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or dedicated video conferencing hardware help enable virtual meetings with remote employees or clients.
- Collaboration platforms: Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Google Workspace streamline internal communication, file sharing, and project management.
3. Ergonomic workstations and equipment
I’m sure you can agree that a poor workstation setup leads to discomfort, fatigue, and reduced efficiency, but ergonomic furniture and high-quality monitors help employees stay comfortable and focused.
Investing in the right equipment not only boosts productivity but also supports long-term well-being.
Examples include:
- Standing desks and adjustable workstations: Ergonomic furniture, including adjustable desks and chairs, to promote better posture and health.
- Dual or ultra-wide monitors: Dual monitors or large ultra-wide screens to increase productivity and ease multitasking.
4. Visitor management system
Supporting busy offices everywhere, digital visitor management systems streamline the check-in process, enhance security, and minimize workplace disruptions, making them essential for modern offices.
Some examples include:
- Self-service kiosks: Digital check-in stations that allow visitors to sign in quickly and notify hosts upon arrival.
- Automated badge printing: Instant visitor badge generation for easy identification and access control.
- Delivery management: Systems that log package drop-offs and notify recipients, reducing front desk interruptions.
- Visitor logs & reporting: Digital records of office visitors for security and compliance purposes.
5. Office security and access control
Balancing security with convenience is crucial in a modern office. Advanced surveillance, smart access control, and strong cybersecurity measures protect both physical and digital assets, giving employees peace of mind while safeguarding company data.
Some examples include:
- Surveillance cameras: High-quality video surveillance systems for security monitoring.
- Access control systems: Key card, biometric, or smartphone-enabled access control systems to manage entry to office spaces.
- Cybersecurity solutions: Firewall, antivirus, and encryption software to protect digital infrastructure and sensitive data.
6. Smart lighting systems
Outdated lighting can waste energy and impact focus, but smart lighting solutions adapt to occupancy and natural light levels, creating a comfortable and energy-efficient workspace.
These systems not only lower costs but also enhance employee well-being. Examples include:
- Automatic lighting control: Smart lighting systems use motion sensors to turn lights on or off based on occupancy. This helps reduce energy consumption and costs.
- Daylight harvesting: Sensors adjust the brightness of indoor lights depending on the amount of natural light, creating an energy-efficient environment.
7. Smart climate control (HVAC Systems)
An uncomfortable office temperature can drain productivity and increase energy costs.
Smart HVAC systems automatically adjust based on occupancy and preferences, ensuring a comfortable and cost-efficient work environment. Examples include:
- Connected thermostats: Smart thermostats that can monitor office temperature and adjust heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for optimal comfort and energy savings.
- Zone control: These systems allow different areas of the office to have customized temperature settings based on occupancy or specific needs.
Dreamy!
8. Occupancy sensors and space utilization
Underutilized office space and overcrowded areas can hurt efficiency and employee experience.
Occupancy sensors and hot-desking solutions provide real-time data to optimize workspace usage, making flexible work arrangements easier to manage. Examples include:
- Room and desk sensors: Sensors can monitor the occupancy of meeting rooms, workstations, and shared spaces. This data helps optimize space usage, reduce overcrowding, and improve workplace planning.
- Hot-desking solutions: Connected systems can manage and allocate desks or workstations dynamically based on employee needs, making it easier for companies with flexible and hybrid work arrangements. Some good office space management software examples include OfficeSpace and Deskfound.
9. Mobile device integration
With employees using personal devices for work, security and connectivity can become challenges.
BYOD support and mobile device management ensure seamless, secure access to office systems, keeping productivity high while protecting sensitive information.
- Bring your own device (BYOD) support: Systems to securely integrate employees’ personal devices with office systems (e.g., secure mobile access to email, and cloud files).
- Mobile device management (MDM): Tools that help manage and secure employee mobile devices used for work.
8 Steps To Choose And Implement New Office Technology
Working in unison, office technologies can create spaces that people love to work in. However, just randomly throwing something into the mix rarely works.
Instead, choosing and implementing new office technology merits a considered approach.
1. Assess your needs
- Identify pain points: Understand the current inefficiencies or challenges in your office environment (e.g., communication issues, slow processes, outdated tools).
- Employee input: Get feedback from employees on the challenges they face and any technologies they think could help.
- Business goals: Align the new technology with your business objectives, whether it’s improving collaboration, scaling operations, making better use of office space, or implementing flexible working.
2. Research and compare solutions
- Determine key features: Based on your needs, identify the must-have features (e.g., cloud storage, automation, security).
- Vendor comparison: Research multiple vendors, comparing their offerings on:
- Price and scalability
- Ease of use
- Customer support and service level agreements (SLA)
- Integration with your existing systems.
- Read reviews: Look for user feedback, case studies, or third-party reviews to validate the performance and reliability of the technology.
3. Set a budget
- Consider the total cost of ownership: Factor in both upfront costs and ongoing expenses like subscriptions, training, maintenance, and upgrades.
- Return on investment (ROI): Estimate how the technology will save time, reduce costs, or improve revenue over time. Dan George's article on HR financial literacy can help here.
4. Involve stakeholders
- Get buy-in: Present your findings to key stakeholders (e.g. leadership team, department heads) and explain the benefits, costs, and risks.
- Collaborative decision-making: Ensure all departments affected by the new technology have a say, especially IT, HR, or finance.
5. Pilot testing (if possible)
- Run a Trial: If possible, choose a small group of employees to test the technology in a real-world setting. This will help you evaluate:
- Ease of adoption
- Compatibility with existing workflows
- Actual vs. expected benefits
- Gather feedback: Collect insights from users on functionality and usability during the pilot phase.
6. Implementation planning
- Develop a rollout plan: Break down the implementation process into manageable steps such as:
- Install and set up the technology
- Migrate data, if necessary
- Integrate with existing systems.
- Guidance and onboarding: Provide comprehensive guidance to ensure employees are comfortable using the new technology. Consider creating user guides or having regular Q&A sessions.
- Communication: Clearly communicate the rollout schedule, expectations, and any changes to workflows or processes.
7. Monitor adoption and performance
- Track usage: Monitor how the new technologies are performing and identify any challenges.
- Collect feedback: Regularly ask for feedback on the new technology to understand any issues or areas for improvement.
- Measure success: Compare the performance metrics with your original objectives (e.g., time saved, reduction in errors, increased collaboration).
8. Evaluate and optimize
- Regular check-ins: Periodically evaluate the technology’s impact on your business. Are you seeing the expected improvements? Is further optimization needed?
- Upgrade and evolve: As your business grows or technology evolves, be prepared to scale or upgrade to meet new demands.
Incoming Tech
Thought I'd end on a fun one and showcase some of the latest office technologies from orgz like Google.
Project Starline
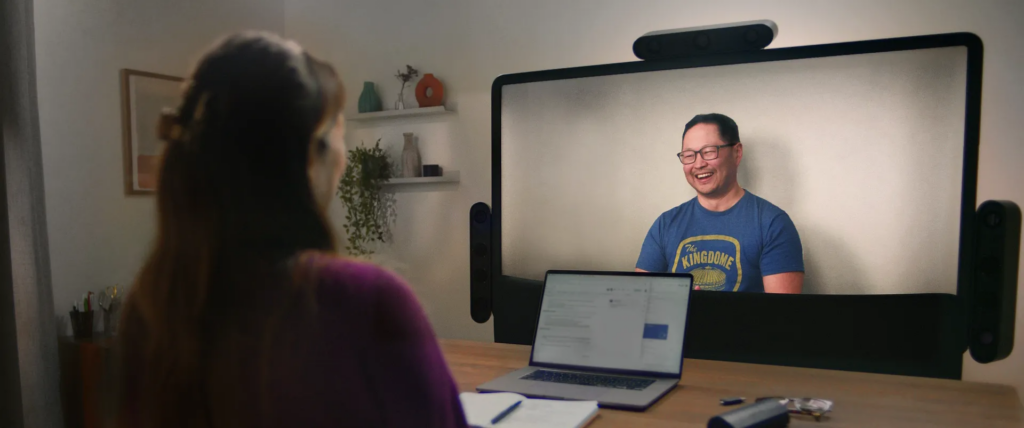

Google's Project Starline offer 3D video communication platforms that create a realistic sense of presence without the need for glasses or headsets. This innovation makes virtual meetings more engaging and reduces video meeting fatigue.
Logitech's Spot
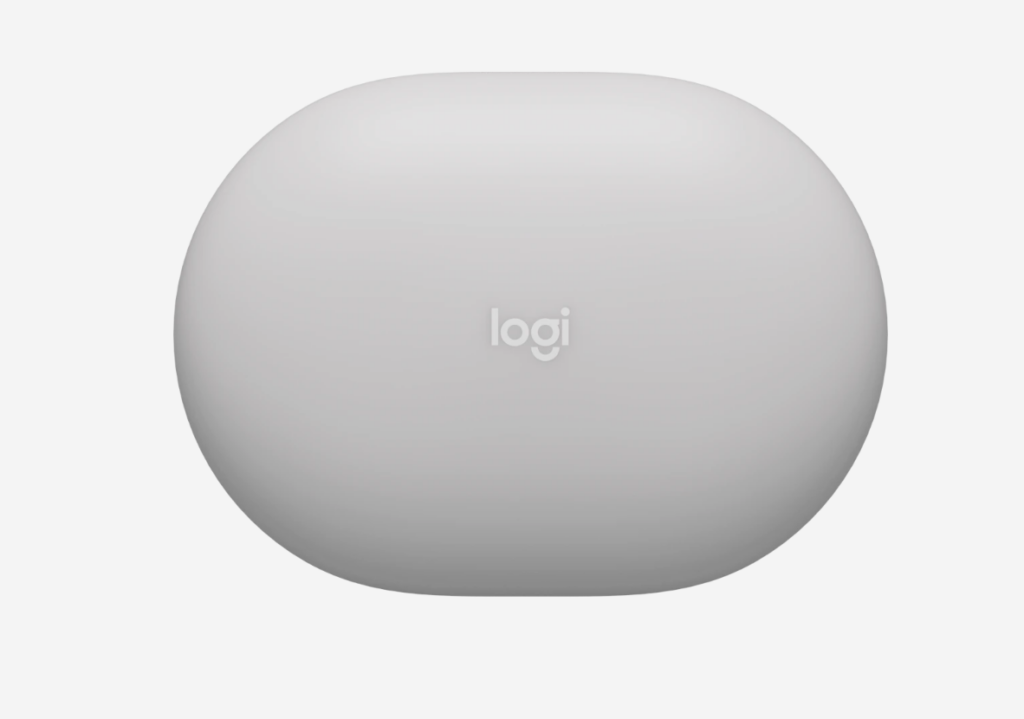

Devices like Logitech's Spot utilize millimeter-wave radar technology to monitor office occupancy and environmental factors such as temperature and air quality.
These tiny sensors help optimize workspace utilization and maintain a healthy office environment by providing real-time data on room usage and conditions.
Office robots
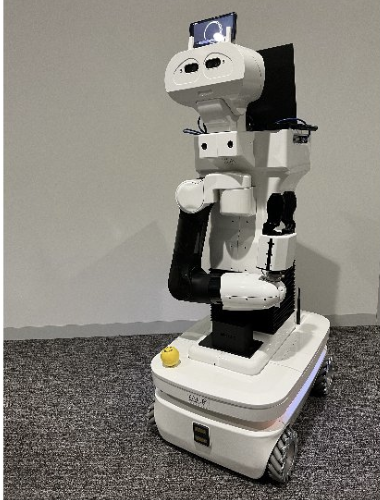
The robots are coming! Robots like "OfficeMate" are being introduced to assist with practical tasks, foster social interaction, and promote health and well-being in office spaces.
A pilot evaluation showed that users see potential in such robots for reducing stress and promoting healthy habits.
Subscribe To The People Managing People Newsletter
The world of office technology is constantly evolving. To keep up to date, subscribe to our weekly newsletter for HR and business leaders. You’ll receive all our latest content to help you grow in your career and make greater impact in your org.




